Introduction to IVF
In Vitro Fertilization, commonly referred to as IVF, is a beacon of hope for millions of couples worldwide facing infertility challenges. This advanced reproductive technology has been revolutionizing the concept of fertility and childbearing since its successful first procedure in 1978.
At its core, IVF is a series of procedures used to assist with the conception of a child. It involves the extraction of eggs, retrieval of a sperm sample, and then manually combining an egg and sperm in a laboratory dish. The embryo or embryos are then transferred to the uterus where they can implant and grow.
IVF can be a preferred treatment option for various fertility obstacles such as blocked or damaged fallopian tubes, male factor infertility, ovulation disorders, or those with a genetic disorder they wish not to pass on.
It is also the go-to solution for women who have had their fallopian tubes removed, couples who have not succeeded with other fertility treatments, or for those who wish to conceive using donor eggs or sperm.

The Science Behind IVF
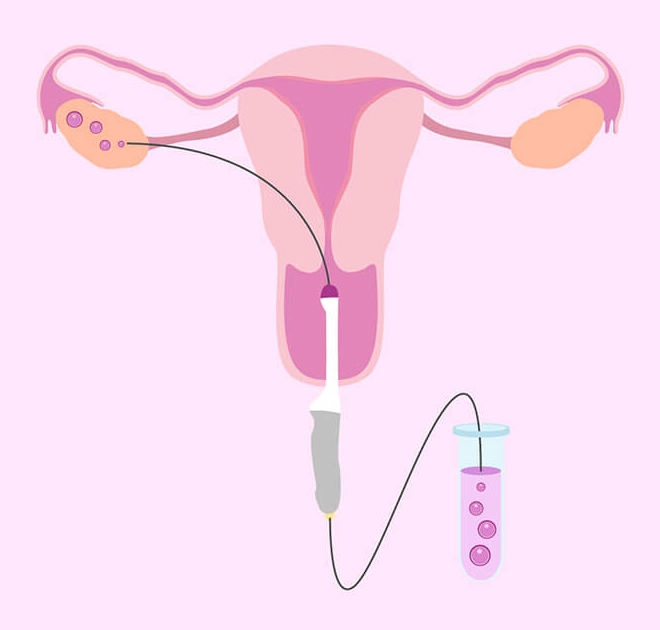
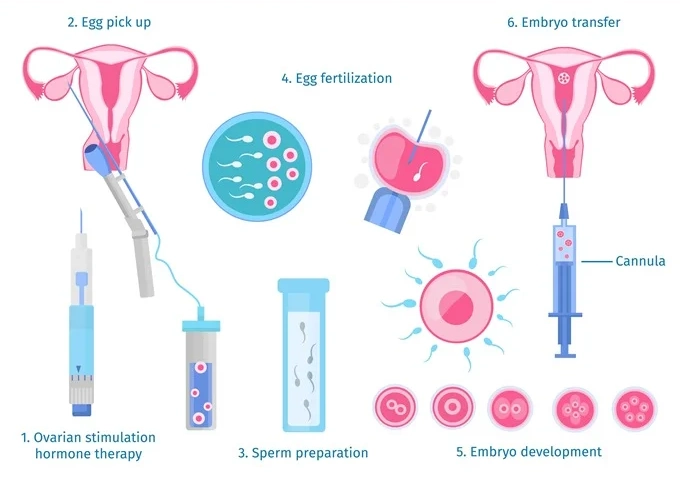
-
Hormonal Stimulation
The IVF process begins with ovarian stimulation, where fertility drugs are used to encourage the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. Normally, a woman produces one egg per menstrual cycle, but IVF requires several eggs to increase the chances of successful fertilization.
-
Egg Retrieval
Once the eggs mature, they are retrieved through a minor surgical procedure known as follicular aspiration. This is typically done under sedation to ensure the comfort of the patient.
-
Sperm Collection
Simultaneously, a sperm sample is collected. In cases of male infertility, advanced techniques like Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) may be employed, where a single sperm is injected directly into the egg.
-
Fertilization
The retrieved eggs and sperm are combined in a controlled laboratory environment to encourage fertilization. This process may take several hours to days, and the embryos are monitored for growth and development.
-
Embryo Culture
The developing embryos are kept in an incubator that mimics the conditions of the human body. During this period, they undergo critical growth phases until they reach a stage where they are ready for implantation.
-
Embryo Transfer
The most viable embryos are selected for transfer into the woman’s uterus. This procedure is non-surgical and is performed using a thin catheter that passes through the cervix.
-
Implantation and Pregnancy
After transfer, implantation occurs when the embryo attaches to the lining of the uterus. If successful, this leads to pregnancy. The process from fertilization to transfer and then to implantation is critical and requires precise timing and conditions.
-
Support and Monitoring
Post embryo transfer, the patient is given hormonal support and monitored for signs of pregnancy through blood tests and ultrasounds. This early stage is crucial, and medical care is provided to ensure the best chances for a successful pregnancy.
Is IVF Right for You?
Medical Considerations
- Blocked or damaged fallopian tubes
- Male factor infertility, including reduced sperm count or motility
- Women with ovulation disorders, premature ovarian failure, or uterine fibroidss
- Individuals with a genetic disorder they do not wish to pass on to their child
- Unexplained infertility
-
Age-Related Fertility
Women's age plays a crucial role in fertility. As the quality and quantity of a woman's eggs decline with age, IVF success rates also vary accordingly. For older women, the use of donor eggs may increase the chances of success.
-
Emotional Commitment
IVF can be emotionally demanding. It requires a significant commitment to the process, which can be full of ups and downs. Emotional support from partners, loved ones, or professional counselors can be beneficial.
-
Time Investment
The process of IVF requires a considerable time commitment for medical appointments, tests, procedures, and the IVF cycle itself. Prospective patients need to consider their ability to commit to this timeframe.
-
Financial Aspect
IVF can be expensive, and multiple cycles may be needed to achieve a pregnancy. It’s important to have a clear understanding of the costs involved and how much of it is covered by insurance, if at all.
-
Health Risks and Success Rates
Understand the potential health risks associated with fertility drugs and procedures, as well as the statistical success rates of IVF for individuals in your age group and with your particular fertility issues.
-
Psychological Resilience
It’s important to be mentally prepared for all possible outcomes, including the possibility of the treatment not resulting in a pregnancy. The psychological impact can be profound, and resilience is key.
-
Lifestyle Adjustments
Lifestyle changes may be necessary to increase the chances of success, such as quitting smoking, reducing alcohol intake, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing stress.
-
Ethical and Moral Considerations
Some may have ethical or moral questions regarding IVF, such as the disposition of unused embryos. It's essential to consider your personal beliefs and values.
-
Long-Term Perspective
Consider the long-term implications of having a child through IVF, including the health of the mother and child and family dynamics.
The IVF Process Step by Step
-
Initial Consultation and Pre-Treatment Evaluation
This involves meeting with a fertility specialist to discuss the IVF process, conduct necessary medical evaluations, and develop a treatment plan.
-
Ovarian Stimulation
You'll take synthetic hormones to stimulate your ovaries to produce multiple eggs—since some eggs will not develop or fertilize after retrieval.
-
Monitoring Progress
Regular clinic visits allow doctors to monitor the development of the follicles (which contain the eggs) through blood tests and ultrasounds.
-
Trigger Injection
When the follicles are ready, a "trigger shot" is given to mature the eggs and start the ovulation process.
-
Egg Retrieval (Oocyte Retrieval)
Eggs are surgically retrieved from the ovaries in a minor procedure called follicular aspiration, usually done under sedation.
-
Sperm Collection
On the day of egg retrieval, a sperm sample is collected from the male partner or a donor.
-
Fertilization
The sperm and eggs are mixed together in the lab, or ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) may be used to inject a single sperm directly into an egg.
-
Embryo Culture
The fertilized egg divides and becomes an embryo. Laboratory staff will monitor the embryo's growth and select the best one(s) for transfer.
-
Embryo Transfer
A few days after fertilization, the embryo(s) are transferred to the uterus in a procedure that doesn’t require anesthesia.
-
Supporting Implantation
You may receive progesterone to help prepare the lining of your uterus to receive the embryo.
-
Pregnancy Test
About two weeks after the embryo transfer, you’ll take a blood test to determine if you are pregnant.
-
Follow-Up
If the test is positive, you’ll have ultrasounds and monitoring. If the cycle is not successful, you may have a consultation to discuss next steps, which might include another cycle of IVF.
Types of IVF Treatments
IVF treatments can vary based on the techniques and technologies used, as well as the individual needs of the patient. The following are are some of the common types of IVF treatments:
-
Conventional IVF
The standard process of stimulating the ovaries, retrieving eggs, fertilizing them in a lab with sperm, and transferring the resulting embryos to the uterus.
-
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
A single sperm is injected directly into an egg to facilitate fertilization, often used when male infertility is a factor.
-
Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET)
Embryos created during a conventional IVF cycle are frozen for future use and can be thawed and transferred to the uterus in a subsequent cycle.
-
Donor Eggs or Sperm
When a couple cannot use their own eggs or sperm, they can use donor eggs, sperm, or embryos.
-
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Embryos are tested for genetic disorders before being transferred to the uterus.
-
Natural Cycle IVF
IVF using the woman’s natural cycle without the use of drugs for ovarian stimulation.
-
Mini IVF or Mild IVF
A lower-dose hormone regimen is used for ovarian stimulation, aiming to produce fewer but higher quality eggs.
-
Assisted Hatching
A laboratory technique in which a small hole is made in the outer layer of the embryo to aid implantation in the uterine lining.
-
Co-Culture
A layer of cells from the mother’s uterine lining is used as a foundation to nurture the embryo before transfer.
-
Surrogacy
Another woman carries the pregnancy to term. The egg and sperm may come from the intended parents or from donors.
Understanding Success Rates
-
Age Factor
Success rates of IVF typically decline as a woman’s age increases, especially after the mid-30s. Younger women usually have higher success rates.
-
Clinic Performance
Research individual clinic success rates, as they can vary. Some may specialize in treating more complex fertility issues or may have more advanced technology.
-
Type of Infertility
The underlying cause of infertility can affect success rates. For instance, issues like uterine abnormalities or male factor infertility may have different success rates.
-
Treatment Variables
The types of IVF treatment (e.g., conventional IVF, ICSI, use of donor eggs) can also influence success.
-
Measurement of Success
Success can be measured in different ways – pregnancy rate per cycle started, per egg retrieval, per embryo transfer, or live birth rate.
-
Multiple Cycles
Cumulative success rates across several cycles are often higher than those for a single cycle.
-
Add-ons
Certain techniques or treatments, such as PGT or assisted hatching, may be suggested to improve success rates in specific cases.
-
Lifestyle Factors
Smoking, weight, alcohol use, and other lifestyle factors can influence IVF outcomes.
-
Statistical Interpretation
Be aware that success rates can be presented in ways that make them appear more favorable. Always ask for clarification on what the statistics represent.
-
National Databases
Check national databases for fertility clinic success rates to get an unbiased picture.
The Role of Genetic Screening
-
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
This term encompasses procedures used to identify genetic defects in embryos created through IVF before pregnancy. PGT aims to prevent certain genetic diseases or disorders from being passed on to the offspring.
-
Types of PGT
PGT-A (Aneuploidy) : Screens for the correct number of chromosomes.
PGT-M (Monogenic/Single Gene Disorders): Tests for specific hereditary genetic diseases.
PGT-SR (Structural Rearrangements) : Looks for embryos with structural chromosome abnormalities. -
Improving Success Rates
By selecting genetically healthy embryos, PGT can potentially increase the chances of a successful pregnancy and decrease the risk of miscarriage.
-
Family Planning
For couples with a known risk of genetic disorders, PGT provides an option to avoid the transmission of the condition to their children.
-
Ethical Considerations
While PGT can help prevent serious genetic diseases, it also raises ethical questions about the selection of embryos based on genetic criteria.
-
Limitations
PGT is not 100% accurate and cannot detect every possible genetic issue. There might be false positives or negatives, and some embryos may be mosaic (a mix of normal and abnormal cells).
-
Cost and Accessibility
Genetic screening can add a significant cost to IVF treatment and may not be covered by insurance. It's also not available in all clinics.
-
Decision Making
Couples should consider the emotional and financial implications of genetic screening. Counseling can help understand the risks, benefits, and potential outcomes of PGT.
-
Legal and Regulatory Framework
The use of genetic screening in IVF is subject to varying regulations in different countries, affecting access and practices.
-
Technological Advances
The field is rapidly evolving, with new techniques enhancing the accuracy and scope of genetic screening.
Risks and Complications of IVF
-
Multiple Births
IVF increases the chance of multiple pregnancies if more than one embryo is transferred. Multiple births carry higher risks of premature labor and low birth weight.
-
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
Some women may react to the hormone drugs used to stimulate egg production by developing OHSS, which can cause swollen, painful ovaries.
-
Ectopic Pregnancy
This occurs when the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most commonly in a fallopian tube. IVF possibly increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
-
Egg Retrieval Complications
The process of retrieving eggs involves inserting a needle through the vaginal wall and into the ovary. This can cause bleeding, infection, or damage to the bowel, bladder, or a blood vessel.
-
Miscarriage
The risk of a miscarriage with IVF is similar to that of a natural conception, but the risk can increase with the mother's age, especially in women over 40.
-
Birth Defects
The age of the mother is the primary risk factor in the development of birth defects, whether conception occurs naturally or through IVF.
-
Emotional and Psychological Impact
IVF can be physically and emotionally draining. The associated stress, along with the hormonal effects of fertility drugs, can lead to psychological complications such as depression and anxiety.
-
Failure of Treatment
Not all IVF cycles result in pregnancy, and failure can be emotionally and financially taxing. The likelihood of success decreases with age, particularly after the mid-30s.
-
Medication Side Effects
Fertility drugs can have side effects, ranging from mood swings and headaches to hot flashes and abdominal pain.
-
Long-term Health Risks
Research is ongoing regarding the long-term health risks of IVF for both the mother and the children, such as increased risk of ovarian cancer or cardiovascular disease.
-
Financial Strain
IVF can be expensive, and multiple cycles may be needed. This financial burden can be a significant source of stress, especially as insurance coverage for IVF varies widely.
Emotional Considerations and Support
Emotional Considerations:
-
Stress and Anxiety
The uncertainty of outcomes and the intense nature of the treatment process can lead to high levels of stress and anxiety.
-
Impact on Relationships
The emotional and physical demands of IVF can strain personal relationships, not just with partners, but also with friends and family.
-
Depression
The hormonal changes due to fertility drugs, coupled with the emotional stress, can contribute to depression in some individuals.
-
Guilt and Self-Blame
It's common for individuals or couples to experience feelings of guilt or self-blame, especially after unsuccessful attempts or complications.
-
Isolation
Couples undergoing IVF may feel isolated or disconnected from others who do not understand their journey.
-
Decision-Making Stress
Decisions regarding the number of embryos to transfer and what to do with unused embryos can be sources of significant stress.
Support Options:
-
Fertility Counseling
Professional counseling from someone who specializes in fertility issues can provide a safe space to discuss emotions and develop coping strategies.
-
Support Groups
Meeting others who are going through similar experiences can provide comfort and reduce feelings of isolation.
-
Online Communities
Online forums and support networks can offer 24/7 access to resources and support from a larger community.
-
Couples Therapy
Attending therapy together can help strengthen the relationship and improve communication during the IVF process.
-
Mind-Body Techniques
Yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can help manage stress and improve overall well-being.
-
Education
Understanding the IVF process can help manage expectations and reduce anxiety.
-
Self-Care
Prioritizing self-care is crucial. This includes healthy eating, regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and finding time for activities that bring joy and relaxation.
-
Financial Planning
Consulting with a financial advisor or using resources provided by fertility clinics can help manage the financial stress associated with IVF treatment.
-
Fertility Coach or Advocate
Some find it helpful to have an advocate or coach who can provide personalized support and guidance throughout the IVF process.
Cost of IVF in India
Base Costs
-
Consultation and Pre-Assessment : Initial consultations and fertility assessments typically incur a charge. These are preliminary steps to determine suitability for IVF.
Medication : The cost of fertility drugs can constitute a significant portion of the total expense. These drugs are used to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs.
Procedure Costs: This includes the costs for egg retrieval, sperm preparation, fertilization, and embryo transfer.
Additional Costs
-
Advanced Techniques: Use of ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection), PGD/PGS (Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis/Screening), or assisted hatching may add to the base cost.
Cryopreservation: Freezing and storage of embryos or sperm will incur additional charges.
Donor Eggs or Sperm: If donor eggs or sperm are needed, this can significantly increase the total cost.
Surrogacy: In cases where a surrogate is required, there are legal and medical costs that can be quite substantial.
Multiple Cycles: Often, more than one IVF cycle is needed, which means repeating the costs for each cycle.
Typical Cost Range:
- The cost for one cycle of IVF in India can range from approximately INR 1,00,000 to INR 3,50,000.
- Some clinics offer package deals for multiple cycles, which can reduce the per-cycle cost.
Insurance and Financing:
-
Insurance Coverage: IVF coverage in health insurance is not very common in India, but some policies may include it, so it's worth checking with your insurer.
EMI Options: Many clinics offer financing options where the cost can be spread over a period, making it more manageable.
Factors Affecting Cost:
-
Location: Metropolitan cities often have higher costs compared to smaller cities.
Clinic Reputation: Renowned fertility centers may charge more due to their higher success rates and advanced technology.
Individualized Treatment: Tailored treatment plans can lead to variations in cost.
Seeking the Best Value:
-
Comparing Clinics: It's important to compare clinics not just on cost, but also on success rates, quality of facilities, and expertise of staff..
Transparent Pricing: Opt for clinics that offer clear, all-inclusive pricing to avoid hidden costs.
Ask for Breakdowns: Request itemized cost breakdowns for the entire procedure to understand where your money is going.
Insurance and Financing Options for IVF in India
Health Insurance Coverage:
-
Limited Coverage
Traditionally, insurance policies in India have not covered infertility treatments like IVF. However, this is gradually changing, and some insurers have started offering coverage for such treatments.
-
Specific Riders:
Look for health insurance plans that offer riders or specific add-ons for IVF treatments. These may come with additional premiums.
-
Corporate Coverage
Some employers may offer health insurance plans that include IVF treatments. Check with your HR department about the scope of your company-provided health insurance.
-
Terms and Conditions
Policies that do cover IVF often have stringent terms and conditions, like waiting periods, limitations on the number of cycles, and age restrictions. Always read the fine print.
Government Schemes:
-
The Indian government has introduced various schemes that provide financial assistance to couples seeking fertility treatments. Check for eligibility criteria and how to apply.
Medical Loans:
-
Flexible Repayment: Loans for medical purposes often have the advantage of flexible repayment options and competitive interest rates.
Personal Savings and Payment Plans:
-
Savings : Some couples turn to crowdfunding platforms to raise money for IVF treatments. These platforms allow you to create campaigns where friends, family, and even strangers can contribute financially.
Payment Plans : Some clinics offer payment plans that allow you to pay for the treatment over a period of time, rather than a lump sum upfront.
Additional Financial Considerations
-
Tax Benefits : Inquire about any tax benefits that may be available for medical treatments, as some expenses may be tax-deductible under Section 80D of the Income Tax Act in India.
Flexible Spending Accounts : If available, use flexible spending accounts (FSAs) or health savings accounts (HSAs) to pay for IVF treatments with pre-tax dollars.
Financial Counseling:
-
Seek assistance from financial counselors who specialize in fertility treatments. They can guide you through the process of understanding costs, insurance benefits, and payment options.
Selecting an IVF Clinic and Specialist in India
-
Reputation and Accreditation:
Clinic Credibility : Research the reputation of the clinic. Look for reviews and testimonials from former patients.
Accreditation : Verify if the clinic is accredited by relevant health authorities such as the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and other regulatory bodies. -
Expertise of Specialists:
Qualifications : Check the qualifications and experience of the IVF specialists. Look for doctors with significant expertise in reproductive medicine.
Success Rates : Inquire about the success rates of the specialists and the clinic overall, specifically for cases similar to yours. -
Technology and Facilities:
Advanced Technology : Ensure that the clinic uses state-of-the-art technology and follows the latest IVF protocols.
Laboratory Standards : The quality of the IVF lab plays a critical role. Confirm that the clinic maintains high standards for its laboratory facilities. -
Personalized Care:
Patient-Centric Approach Choose a clinic that offers a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Support Staff : The presence of caring and supportive staff can make a significant difference in your IVF journey. -
Ethical Practices:
Transparent Practices Transparency in the clinic's procedures, success rates, and costs are essential.
Ethical Standards : Make sure the clinic follows the ethical guidelines set forth by medical authorities, especially concerning sensitive issues like embryo handling and storage. -
Consultation Experience:
Initial Consultation : The quality of the initial consultation can be indicative of the clinic's approach. Did the specialist take the time to answer all your questions thoroughly?
Communication : Look for specialists who communicate clearly and are readily available to address concerns during the treatment process. -
Location and Convenience:
Accessibility : Consider the clinic's location, as IVF requires frequent visits. Proximity can reduce travel-related stress and costs.
Operational Hours : Clinics with flexible operational hours can accommodate your schedule better. -
Cost Transparency:
Detailed Breakdown : Ensure the clinic provides a detailed cost breakdown without any hidden charges.
Package Deals : Some clinics offer package deals that might reduce the overall cost of the treatment. However, scrutinize these packages carefully. -
Second Opinions
Consulting Peers : Don't hesitate to seek a second opinion if you have doubts. It can provide reassurance or offer alternative perspectives.
-
Personal Comfort:
Ultimately, your comfort with the specialist and the clinic environment is crucial. Trust your instincts when it comes to your final choice.
-
Additional Services:
Counseling Services : Check if the clinic provides emotional and psychological counseling, which is an essential part of IVF treatment.
Aftercare and Follow-Up Post IVF Treatment
-
Post-Procedure Monitoring:
Initial Rest : Immediately following embryo transfer, patients are usually advised to rest for a brief period.
Early Symptoms : The clinic will provide guidelines on recognizing early signs of both success (such as a positive pregnancy test) and complications (such as ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome). -
Pregnancy Testing:
Blood Tests : Patients will be scheduled for blood tests to measure hCG levels to confirm pregnancy, generally two weeks after embryo transfer.
Follow-up Ultrasounds : If pregnant, early ultrasounds will be scheduled to confirm the viability of the pregnancy and monitor for multiples. -
Emotional Support:
Counseling : Many clinics offer counseling services to help cope with the emotional stress post IVF, regardless of the outcome.
Support Groups : Engaging with IVF support groups can provide comfort and understanding from people who have undergone similar experiences. -
Physical Health:
Activity Level: Clinics usually advise on when normal activities can be resumed.
Diet and Medication : The specialist may recommend continuing certain medications and maintaining a healthy diet to support a potential pregnancy. -
Handling Outcomes:
Success If the treatment is successful, the IVF clinic will coordinate with an obstetrician for prenatal care.
Non-Success : In cases where IVF does not result in pregnancy, the clinic may offer a review consultation to discuss the next steps, which could include another cycle of IVF. -
Follow-Up Appointments:
Review Consultations: These are essential to discuss the outcomes of the cycle and plan future treatment strategies.
Health Check-Ups : Regular health check-ups may be recommended to monitor the patient’s well-being. -
Medication Review:
Hormonal Support: If pregnant, progesterone support might continue to sustain the uterine lining.
Adjustment of Medications : Depending on the outcome, medication regimens may be adjusted. -
Future Fertility Planning:
Debriefing: The specialist will discuss the cycle's insights, which helps in planning future fertility treatments.
CryopreservationIf there are additional embryos, the clinic will discuss options for freezing and storage. -
Lifestyle Advice:
Continued Care : Recommendations for maintaining a healthy lifestyle post IVF are provided.
Stress ManagementTechniques for managing stress and ensuring mental well-being will be advised. -
Accessibility of the Clinic:
Open Line of Communication: Clinics often ensure that patients can reach out with any post-procedure questions or concerns.
Emergency ContactPatients should be given an emergency contact number for any urgent issues that may arise. -
Record Keeping:
Documenting the Process: It's important to keep detailed records of the IVF cycle, treatments, and outcomes for future reference.
Lifestyle and Diet Considerations Post IVF Treatment
-
Nutritional Support:
Balanced Diet : Emphasize a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Folic Acid : Continue taking folic acid supplements as advised to support early fetal development.
Hydration : Ensure adequate fluid intake to stay hydrated, which is particularly important during pregnancy. -
Weight Management:
Healthy Weight :Strive to maintain a healthy weight, as extremes in body weight can affect hormone levels and pregnancy outcomes.
Regular Exercise : Engage in moderate exercise to maintain fitness and manage weight, but avoid high-intensity workouts unless cleared by the physician. -
Lifestyle Adjustments:
Stress Reduction : Implement stress-management techniques such as yoga, meditation, or mindfulness practices.
Support Groups : Prioritize sleep for 7-9 hours per night to aid in hormonal balance and overall well-being.
No Smoking or Alcohol : Avoid tobacco and alcohol consumption, as they can negatively impact fertility and pregnancy. -
Dietary Restrictions:
Caffeine Intake : Limit caffeine intake to a moderate level, as high consumption can be detrimental to fertility and pregnancy.
Avoid Raw Meat : To reduce the risk of infections, avoid raw or undercooked meat, and ensure all fruits and vegetables are washed thoroughly.
Limit Processed Foods : Reduce the intake of processed foods and those high in sugar and unhealthy fats. -
Supplementation:
Prenatal Vitamins: Continue taking any prescribed prenatal vitamins to support pregnancy.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids : Consider omega-3 supplements (like those from fish oil) to support fetal brain development, but only after consulting the doctor. -
Traditional Remedies:
Ayurveda and Traditional Medicine: Some may opt for traditional dietary practices or Ayurvedic remedies. It's essential to discuss these with the IVF specialist to ensure they don't interfere with treatment outcomes.
-
Food Safety:
Food Hygiene: Practice good food hygiene to prevent foodborne illnesses, which can be more severe during pregnancy.
Listeria Avoidance : Steer clear of foods with a high risk of listeria contamination, like unpasteurized dairy products and certain cold meats. -
Regular Monitoring:
Blood Sugar Levels: Monitor blood sugar levels if there's a history of diabetes or gestational diabetes.
Blood Pressure : Keep track of blood pressure, as hypertension can affect pregnancy outcomes. -
Emotional Well-being:
Positive Environment: Create a positive and supportive environment, as emotional wellness can impact physical health.
Professional Support: Seek professional support if you experience emotional distress or signs of depression or anxiety. -
Physician Consultation:
Dietary Changes: Discuss any major dietary changes with your healthcare provider to ensure they align with your health needs during and after IVF treatment.
Regular Check-Ups: Attend all scheduled post-IVF check-ups and consult your doctor before starting any new dietary supplements or exercise regimes.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies Post IVF Treatment
-
Yoga and Meditation:
Yoga :Practicing gentle yoga can help reduce stress, increase blood flow to the reproductive organs, and balance hormone levels.
Meditation : Meditation and breathing exercises can help manage the stress and anxiety that often accompany fertility treatments. -
Acupuncture:
Fertility Acupuncture: Some studies suggest that acupuncture can improve blood flow to the ovaries and uterus, potentially increasing the chances of implantation.
-
Ayurveda:
Herbal Remedies : Ayurvedic herbs like Ashwagandha and Shatavari are believed to support fertility and vitality.
Panchakarma : Detoxification processes in Ayurveda might be recommended for overall health optimization, but it’s crucial to consult with an IVF specialist before undergoing any such treatment. -
Homeopathy:
Constitutional Treatment : Homeopathic remedies may be tailored to the individual’s constitution, aiming to enhance general health, which could indirectly support fertility.
-
Naturopathy:
Dietary Changes : Naturopathic doctors may suggest specific diets that support fertility, alongside other lifestyle changes.
Supplements : Natural supplements like coenzyme Q10, vitamin D, and others might be recommended to support reproductive health. -
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM):
Herbs and Diet : TCM practitioners may prescribe herbs and dietary modifications believed to nourish the body’s vital energy (Qi) for conception.
-
Aromatherapy:
Essential Oils: Certain essential oils are used in aromatherapy to promote relaxation and alleviate stress.
-
Chiropractic Care:
Spinal Adjustments: Some believe that chiropractic adjustments can help optimize body functions by improving spinal alignment and nerve communication.
-
Reiki and Energy Healing:
Energy Work : Techniques like Reiki are intended to help balance the body’s energies, reduce stress, and promote emotional well-being.
-
Biofeedback:
Stress Management : Biofeedback can help individuals learn to control physiological functions and manage stress levels, which could be beneficial post-IVF.
-
Mind-Body Therapies:
Counseling and Support Groups : Psychological support through counseling and fertility support groups can help manage the emotional aspects of the IVF journey.
Considerations for Alternative Therapies
-
Consult Healthcare Providers
Always consult with IVF specialists before starting any alternative therapies to avoid any potential interference with conventional treatments.
-
Evidence and Safety
Research the evidence supporting the use of any alternative therapy and consider its safety, especially in the context of fertility treatments.
-
Integration with Conventional Care
These therapies should complement, not replace, the recommendations and treatments provided by medical professionals.
-
Qualified Practitioners
Seek out certified and experienced practitioners in any alternative therapy field.
Frequently Asked Questions
Sex selection is technically possible through preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD); however, it is illegal in India and not done in India.

