Introduction to Total Knee Replacement
Total Knee Replacement (TKR), also known as Knee Arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure that is performed to replace the worn-out or damaged surfaces of the knee joint. This surgery is typically recommended for patients suffering from severe arthritis or a serious knee injury. Over the years, TKR has evolved with advancements in surgical techniques and prosthetic design, significantly improving the outcomes for patients.
The goal of a Total Knee Replacement is to relieve pain, restore alignment and function, and return patients to their normal activities with improved quality of life. During the procedure, the orthopedic surgeon removes the damaged cartilage and bone from the surface of your knee joint and replaces them with an artificial joint made from metal and plastic composites. This artificial joint is designed to replicate the knee’s natural movement.
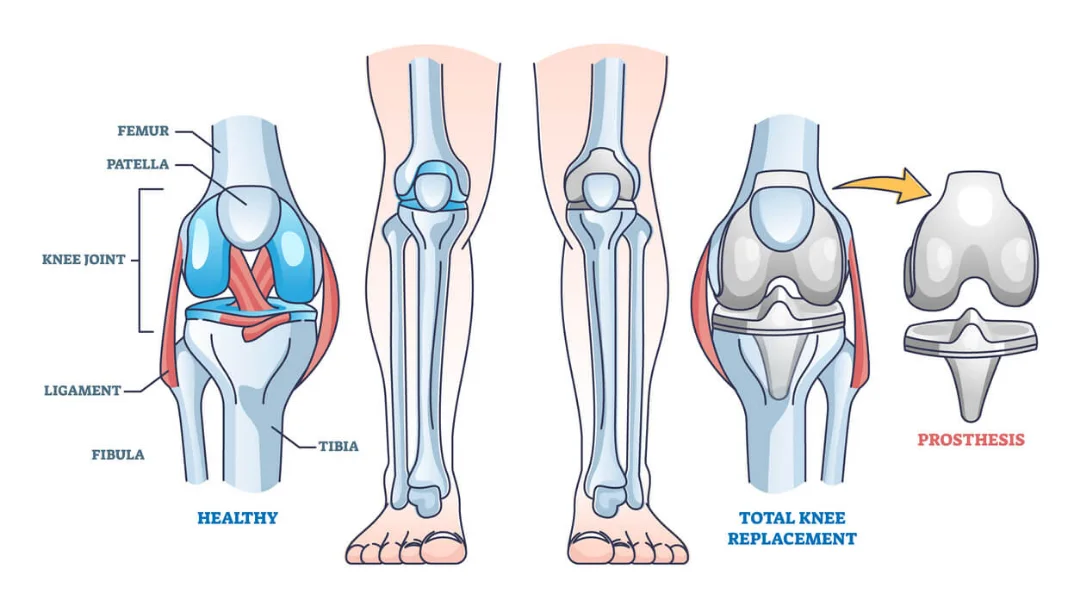
Knee replacement is one of the most successful procedures in all of medicine, with hundreds of thousands of surgeries performed each year globally. It is a safe and effective procedure that can relieve pain, correct leg deformity, and help patients resume normal activities.
The decision to proceed with knee replacement surgery is a cooperative one between you, your family, your primary care doctor, and your orthopedic surgeon. The process leading to surgery is multifaceted, involving a comprehensive evaluation, a detailed explanation of the procedure, understanding the recovery process, and considering the overall impact on the patient’s life.
The journey to a new knee begins with understanding your condition and the treatment options available. With successful surgery and rehabilitation, Total Knee Replacement can be a life-transforming procedure, allowing individuals to regain lost mobility and enjoy a pain-free life.
Understanding Knee Joint Degeneration
Knee joint degeneration is the progressive loss of the smooth cartilage that covers the ends of the bones in the knee joint. This cartilage serves as a cushion and enables frictionless movement of the joint. When it wears down, bones may rub against each other, causing pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility — a condition often referred to as osteoarthritis.
The degeneration can be due to a variety of factors, including
-
Age
The natural aging process can lead to wear and tear of the knee joint over time.
-
Weight
Being overweight or obese puts extra pressure on knee joints, especially during movement.
-
Gender
Women over the age of 55 are more prone to developing osteoarthritis.
-
Injuries
Previous injuries such as fractures, ligament damage, or meniscus tears can lead to joint degeneration.
-
Repetitive Stress
Jobs or sports that put repetitive stress on the knee joint can contribute to cartilage breakdown.
-
Genetics
A family history of osteoarthritis or congenital bone deformities can predispose individuals to knee degeneration.
-
Bone Misalignments
Misaligned bones can cause uneven stress and wear on the knee.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis
An autoimmune condition that can cause inflammation and degeneration of the cartilage.
-
Metabolic Diseases
Conditions like gout and pseudogout can lead to crystalline deposits in the knee joint, leading to degeneration.
As the cartilage deteriorates, the synovial fluid that lubricates the joint becomes less effective, and the space between the bones may narrow. This can result in bone spurs (osteophytes) and can contribute to the pain and loss of function.
Patients with knee joint degeneration may experience symptoms like aching pain, stiffness after periods of inactivity or rest, swelling and warmth in the joint, decreased mobility, and a crunching or grinding sound during movement.
Understanding knee joint degeneration is pivotal for early intervention and to prevent further damage. Treatment options can vary from conservative methods like weight management and physiotherapy to medical interventions including corticosteroid injections and ultimately, surgical options such as Total Knee Replacement when the joint’s condition severely impacts the patient’s quality of life.
Indications for Total Knee Replacement
-
Severe Knee Pain
Pain that limits or completely prevents everyday activities, including walking, climbing stairs, and even resting or sleeping.
-
Moderate to Severe Pain While Resting
This level of pain is present even during rest and at night, often indicating more advanced joint degeneration.
-
Chronic Inflammation and Swelling
Persistent inflammation that does not improve significantly with medication or rest.
-
Knee Deformity
A bowing in or out of the knee that signifies advanced joint disease or deterioration.
-
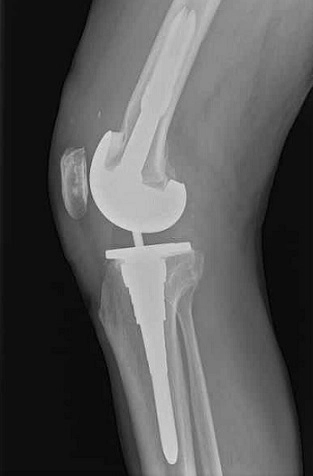
Degenerative Joint Disease
Severe osteoarthritis is a prime reason for TKR, especially when it leads to joint space narrowing and bone damage.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis
When the immune system attacks the lining of the joint, causing pain and stiffness.
-
Post-traumatic Arthritis
Arthritis that develops after an injury to the knee, such as a fracture or ligament damage, which has altered the joint structure.
-
Failed Previous Knee Surgery
When less invasive surgeries like arthroscopy or partial knee replacements have not been successful.
-
Ineffective Non-Surgical Treatments
When medications, physical therapy, knee injections, and the use of walking supports no longer effectively manage knee symptoms.
-
Reduced Quality of Life
When the knee pain and dysfunction significantly impair one’s ability to perform routine activities and affect their quality of life.
Types of Knee Replacement Surgeries
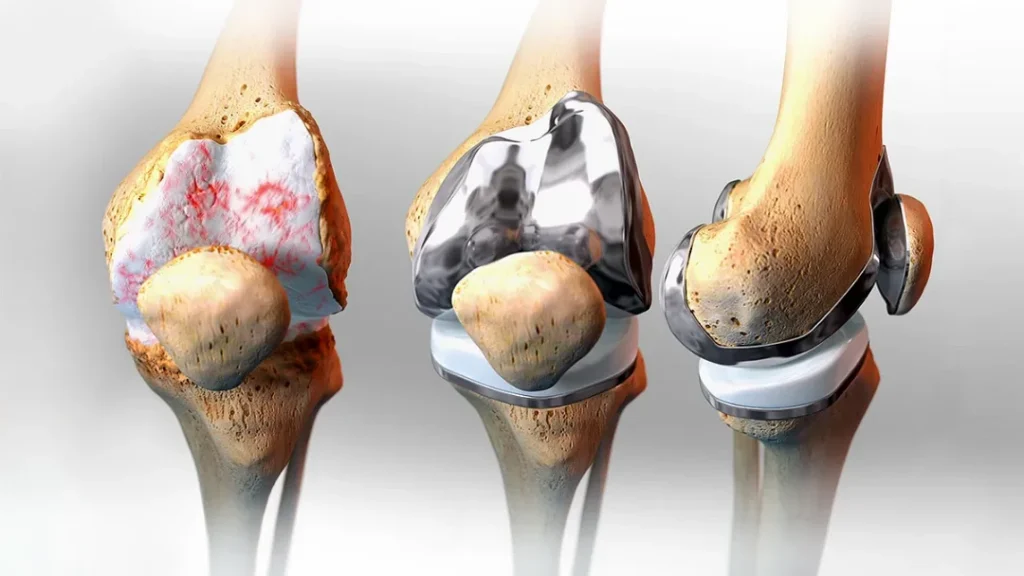
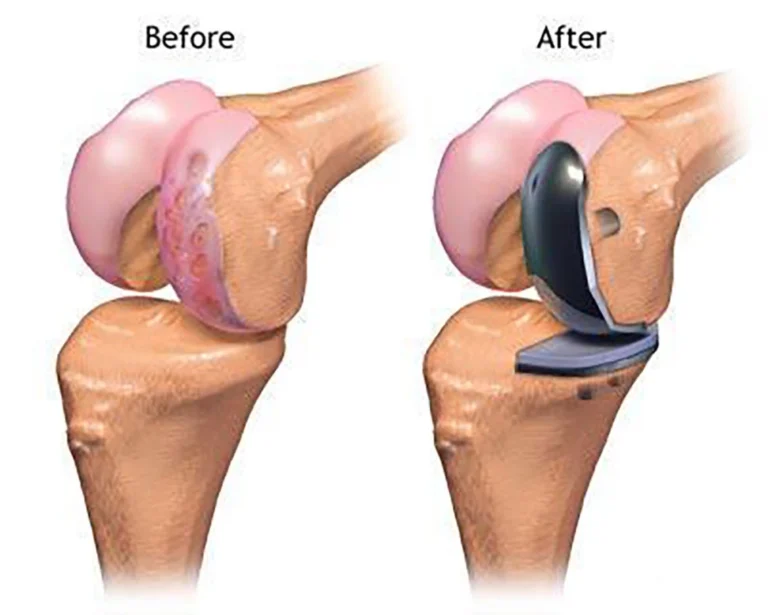
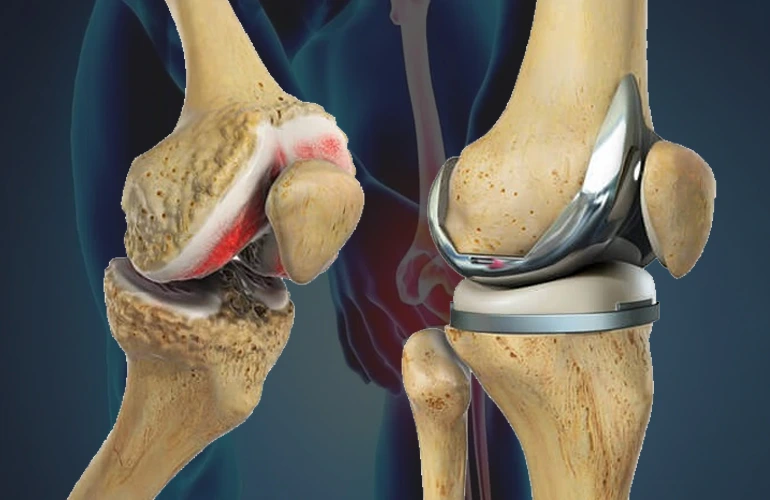
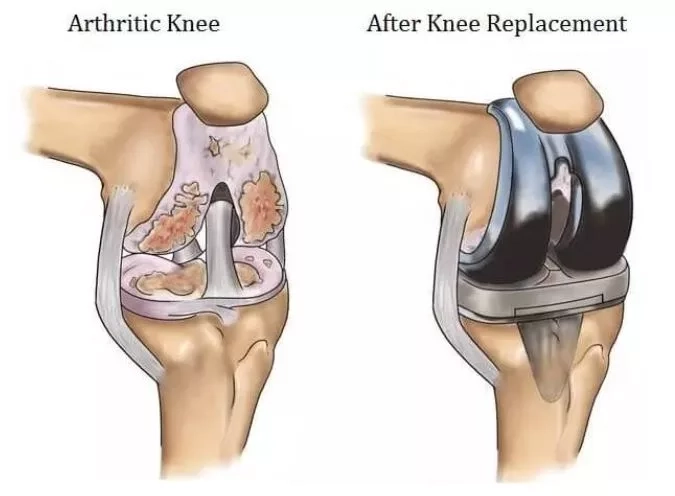
-
Total Knee Replacement (TKR):
This is the most common type of surgery, where all the weight-bearing surfaces of the knee joint are replaced with an artificial implant. It’s suitable for patients with severe arthritis affecting multiple compartments of the knee.
-
Partial Knee Replacement (PKR):
Also known as unicompartmental knee replacement, this procedure involves replacing only one part of the knee joint (either the medial, lateral, or patellofemoral compartment). It’s best for patients whose damage is limited to a specific area of the knee.
-
Revision Knee Replacement:
This surgery is done to replace an old knee prosthesis that has become loose, infected, or worn out.
-
Kneecap Replacement (Patellofemoral Arthroplasty):
This is the replacement of just the underside of the kneecap and the groove it sits in when it’s the only area affected by arthritis.
-
Complex or Revision Knee Replacement:
This is required for patients with severe bone loss or deformity, often due to previous surgeries, severe arthritis, or fractures. It involves more extensive reconstruction.
-
Computer-Assisted Surgery (CAS):
Technological advancements have led to the development of CAS, which provides the surgeon with real-time 3D images of the knee joint during surgery for more precise implant placement.
-
Robot-assisted Knee Replacement:
In this type, a robotic arm is used to assist the surgeon in the removal and replacement of joint components, enhancing precision and potentially improving outcomes.
-
The type of knee replacement surgery is chosen after thorough diagnostic imaging, consideration of the patient's lifestyle, and personal goals post-surgery.
The objective is always to restore function, reduce pain, and improve the quality of life for the patient.
Preparing for Your Knee Replacement
The journey to a successful knee replacement begins well before the surgery day. Adequate preparation can ensure a smoother operation and recovery. The following are steps to prepare for your knee replacement:
-
1. Preoperative Medical Evaluation
A comprehensive health check, including blood tests, cardiac workup, and a review of medications, will be conducted to optimize your health status for surgery.
-
2. Physical Preparation
Strengthening exercises may be prescribed to improve surgical outcomes. Building upper body strength can also be beneficial for mobility during recovery.
-
3. Home Arrangements
Make sure your home is ready for your post-surgery needs. This may include installing safety bars in the shower, securing rugs to prevent slips, and creating a living space on ground level to avoid stairs.
-
4. Nutritional Planning
A well-balanced diet can aid in healing. Pre-planning meals for post-surgery, possibly with the help of a nutritionist, can ensure you get the necessary nutrients without the stress of meal preparation.
-
5. Equipment
Obtain any equipment you'll need post-surgery such as a walker, cane, or raised toilet seat. Learning how to use these aids in advance can be helpful.
-
6. Support System
Arrange for help around the house for a few weeks post-surgery. This includes assistance with cooking, cleaning, and transportation.
-
7. Anesthesia Discussion
You will meet with the anesthesiologist to discuss the types of anesthesia available and determine the best option for your situation.
-
8. Medication Review
Some medications may need to be paused or adjusted before the surgery. Discuss all your medications with your doctor, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
-
9. Quitting Smoking
Smoking can delay wound healing and recovery. If you smoke, it's advisable to quit several weeks before the surgery.
-
10. Mental Preparation
Mental resilience can significantly impact your recovery. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation or counseling can be beneficial.
-
Preparing for knee replacement is not solely about the surgical procedure; it's also about setting up a conducive environment for recovery and ensuring that you, as the patient, are mentally and physically ready for the journey ahead.
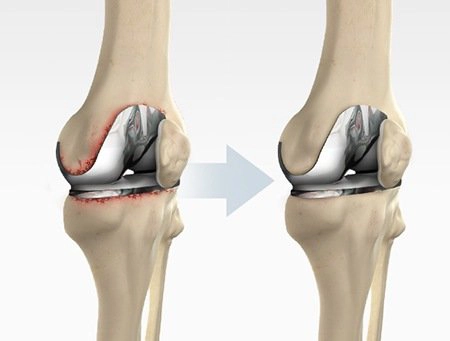
The Knee Replacement Procedure
Total knee replacement, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure where the damaged knee joint is replaced with artificial components.
A step-by-step breakdown of the procedure is as follow,
-
Anesthesia
The procedure usually requires general anesthesia, so you will be asleep and feel no pain. In some cases, spinal or epidural anesthesia may be used to numb the lower body.
-
Incision
The surgeon makes an incision in the knee area to access the joint.
-
Removal of Damaged Joint Surfaces
The damaged cartilage surfaces at the ends of the femur and tibia are removed along with a small portion of the underlying bone.
-
Preparation of Joint Surface
The newly exposed surfaces of the femur and tibia are then prepared to fit the specifically designed metal or ceramic components that will mimic the function of the knee.
-
Implanting the Prosthesis
The metal implants are either cemented or "press-fit" into the bone. The surgeon will choose the method that's best for your situation.
-
Resurfacing the Patella
Depending on the case, the underside of the patella (kneecap) may be cut and resurfaced with a plastic button.
-
Inserting a Spacer
A medical-grade plastic spacer is inserted between the metal components to create a smooth gliding surface.
-
Closing the Incision
Once the components are fixed in place, the incision is closed with sutures or staples.
-
Postoperative Care:
You’ll be moved to a recovery area where you’ll be closely monitored as you recover from anesthesia.
Benefits of Knee Replacement
-
Pain Relief
The most immediate and impactful benefit for patients is the substantial reduction or complete elimination of knee pain.
-
Improved Mobility
Patients often experience a significant improvement in mobility, allowing them to participate in daily activities with greater ease and comfort.
-
Correction of Deformity
Knee replacement can correct leg deformity by realigning the legs to their natural position.
-
Enhanced Quality of Life
With pain relief and improved mobility, patients generally find a marked improvement in their overall quality of life.
-
Increased Activity Level
Many patients are able to return to activities such as walking, swimming, biking, and other low-impact sports they previously found difficult or impossible.
-
Long-term Solution
Knee replacements can last for many years, with modern prostheses often lasting 15-20 years or more, making it a long-term solution to knee problems.
-
Improved Mental Health
Chronic pain is often associated with depression and anxiety; relief from pain can lead to significant improvements in mental health.
Potential Risks and Complications of Knee Replacement
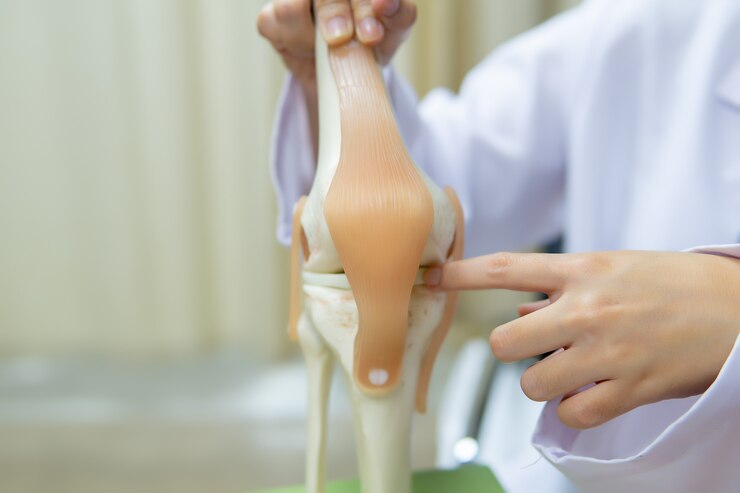
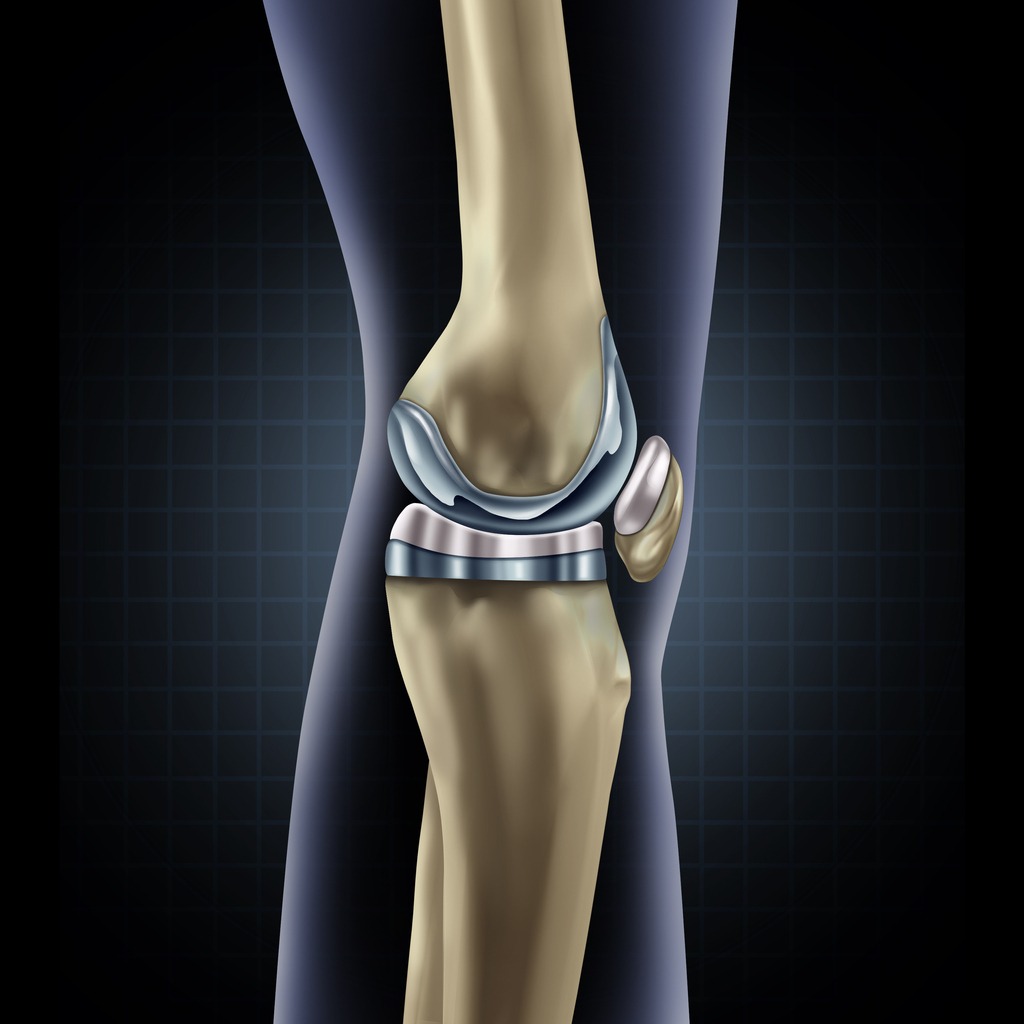
-
Infection
Although rare, there is a risk of infection at the site of the incision or within the joint space.
-
Blood Clots
The formation of blood clots in the veins of the leg (deep vein thrombosis) can be a serious complication, with the potential for clots to travel to the lungs (pulmonary embolism).
-
Implant Problems
While modern implants are durable, they can wear down or loosen over time, potentially requiring a revision surgery.
-
Nerve Damage
During surgery, nerves around the knee may be damaged, potentially leading to numbness or changes in sensation.
-
Blood Vessel Injury
Blood vessels near the surgical site can be injured, leading to bleeding and vascular complications.
-
Anesthesia Risks
Reactions to anesthesia or problems from medications used during surgery can occur.
-
Stiffness
Some patients may experience stiffness in the knee, which might require additional therapy or interventions.
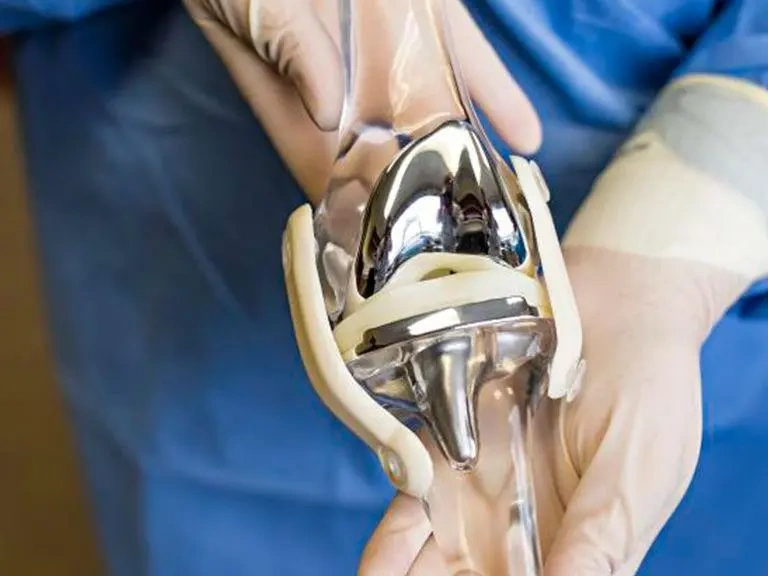
-
Pain
Not all patients achieve complete relief from pain after surgery, and some may continue to experience some level of discomfort.
-
Allergic Reactions
On rare occasions, patients might have an allergic reaction to the metal components in the artificial joint.
-
Fracture
A fracture of the bone around the implant may occur during or after surgery, possibly requiring further surgical intervention.
Recovery and Rehabilitation After Knee Replacement
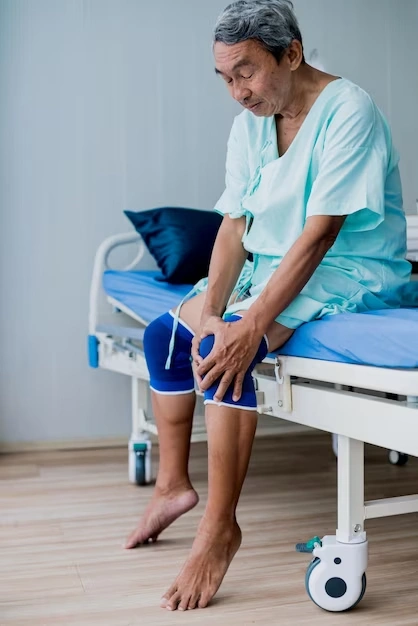

-
1. Immediate Postoperative Period
Initially, patients will spend a few hours in the recovery room. As the anesthesia wears off, efforts to control pain and prevent complications, such as blood clots, begin.
-
2. Hospital Stay
Most patients stay in the hospital for 1 to 3 days post-surgery. During this time, pain management is a priority, and mobility is encouraged as soon as possible with the help of physical therapists.
-
3. Physical Therapy
A physical therapist will guide patients through exercises to strengthen the knee and restore movement. This may start with simple activities like dangling the legs over the side of the bed and progress to standing and walking with assistance.
-
4. Pain Management
Patients will receive medications to manage pain. It's crucial to control pain to participate effectively in physical therapy.
-
5. Home Recovery
Once home, patients should continue with prescribed exercises, increase their activity level gradually, and monitor the surgical site for signs of infection.
-
6. Follow-Up Care
Regular follow-up appointments with the orthopedic surgeon are important to monitor the healing process and the functioning of the knee implant.
-
7. Ongoing Rehabilitation
Outpatient physical therapy usually continues for weeks to months, focusing on improving range of motion, strength, and functional mobility.
-
8. Lifestyle Modifications
Patients are advised to avoid high-impact activities to prolong the life of the implant but are encouraged to engage in low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or cycling.
-
9. Long-Term Recovery:
Full recovery and the return to regular, daily activities can take 3 to 6 months, with continual improvement up to a year post-surgery.
-
10. Support Systems
Utilizing support from home health services, outpatient therapists, and community resources can be beneficial for a smooth recovery.
-
Each patient’s recovery timeline will vary based on their health, the complexity of the surgery, and their commitment to the rehabilitation process. The ultimate goal of recovery and rehabilitation is to return to a more active and pain-free lifestyle
Cost and Insurance Considerations for Knee Replacement in India
-
1. Procedure Cost Variability
The cost for total knee replacement surgery in India can vary widely depending on factors like the choice of hospital, city, type of implant, surgeon's fees, and the extent of surgery needed.
-
2. Hospital Type and Location
Multi-specialty hospitals in metropolitan cities may charge more than smaller, specialized centers in less urban areas, reflecting differences in infrastructure and the cost of living.
-
3. Type of Implant
The choice between a standard implant and a more advanced option can significantly affect the overall cost. Advanced implants, which may offer greater longevity and range of motion, tend to be more expensive.
-
4. Surgeon's Expertise
Renowned and highly experienced orthopedic surgeons may charge higher fees, which contribute to the surgery's total cost.
-
5. Insurance Coverage
Many health insurance policies in India cover knee replacement surgery. However, it is important to check the specifics of your policy regarding coverage limits, co-pays, and deductibles.
-
6. Pre- and Postoperative Expenses
Beyond the surgery itself, patients must consider the cost of preoperative consultations, postoperative rehabilitation, medication, and potential home care services.
-
7. Cashless Facility
Some hospitals offer a cashless facility if they have a tie-up with the patient's health insurance company, which can streamline the payment process.
-
8. Additional Costs
Miscellaneous costs such as hospital stay, operating room fees, anesthesia, and surgical accessories should also be accounted for.
-
9. Financial Planning
It's advisable for patients to speak with hospital billing departments and insurance providers to obtain a detailed understanding of the anticipated costs and coverage.
-
10. Hidden Costs
Patients should inquire about potential hidden costs, such as extended hospital stays, unexpected medical complications, and additional post-surgery therapies.
-
11. Package Deals
Some hospitals offer comprehensive packages for knee replacement that cover a range of services, which can be more cost-effective than paying for each service individually.

